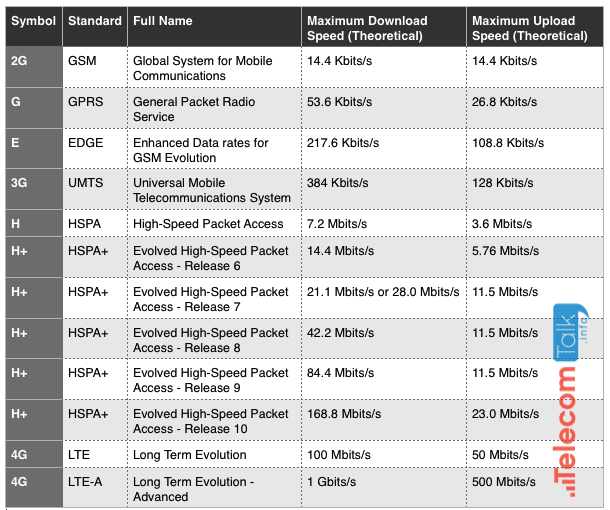
In your Android smartphone, the strength of mobile Internet signal is shown using alphabet letters like G, E, 2G, 3G, H and 4G near the signal bar. These symbols are visible right next to the signal strength indicator. Have you ever wondered about the meaning of these symbols / letters? Well, today I will tell you about the meaning of letters G, E, 2G, 3G, H and 4G in context of the mobile Internet. SEE ALSO: Tips for saving mobile internet data Following image shows the signal bar of a typical Windows based mobile phone. This article informs you about the icon number 2 —which denotes the type of mobile connectivity you’re getting: Letter G stands for GPRS (General Packet Radio Service). It indicates the slowest speed of Internet data transfer in your mobile phone. When you see G near your signal strength indicator, it is certain that your net connection is working at the slowest speed. GPRS is considered to be the second generation (2G) mobile technology. It is the slowest and oldest among all mobile technologies. It is mainly good enough for sending text messages using apps like WhatsApp. Data rates in GPRS are between 56 and 114 kbit/second. If your mobile signal is weak, you might get even slower speed on Internet. There are ways to boost mobile signal strength and thus the Internet speed. Letter E stands for EDGE (Enhanced Data Rates for GSM Evolution). It is also called Enhanced GPRS. This technology lies somewhere in between 2G and 3G technology. So, some people refer to it as 2.5G. EDGE is faster than GPRS but still not good enough to browse the Internet. It takes lot of time in loading websites when your signal bar is showing E letter alongside. Typically EDGE provides a data rate of 400 kbit/second but in ideal conditions data rate of upto 1 Mbit/second can also be achieved. This technology also lies somewhere in between 2G and 3G. Those who call GPRS as 2.5G, they refer EDGE as 2.75G. 3G means the third generation of mobile telephone technology. It uses the Universal Mobile Telecommunications System and is based on GSM standards. Typically 3G provides data transfer rates 384 kbit/second. But depending upon how it is implemented in various networks, the data rate can go upto 42 Mbits/second. Usually 3G is faster than EDGE and you can easily browse websites and stream music. H stands for HSPA (High Speed Packet Access). It is an enhanced form of 3G technology. HSPA provides higher data transfer rates than the basic 3G. Note: In the above comparison chart, all the data speeds are given in terms of bits (e.g. kilobits, megabits etc.) In order to get the speed in terms of bytes (e.g. kilobytes, megabytes etc.) you would need to divide the shown figures by 8. One byte = 8 bits. HSPA can provide peak data rates of up to 14 Mbit/s for downlink and 5.76 Mbit/s for uplink. High-Speed Downlink Packet Access (HSDPA) is a further enhanced version of HSPA. HSDPA supports download speed of up to 99.3 Mbit/s. When you see letter H near the signal bar in your mobile phone, you can stream music and even YouTube videos without much interruption. But if you want to download a movie, it is going to take a very long time! This is enhanced HSPA. It is faster than basic HSPA (as explained above). Relatively speedier data transfer in H+ will make your video to download or stream much more smoothly. At present, 4G technology is not very widely available. So, in most parts of the world, HSPA+ is the fastest speed you can get through mobile Internet. WCDMA is also a 3G technology. It stands for Wide-band Code-Division Multiple Access (CDMA). Interestingly, this technology is actually used in the GSM systems. WCDMA in GSM increases the data transmission speed by using the air interface of CDMA. International Telecommunications Union has adopted WCDMA. If you see 4G near the signal bar in your mobile phone, you’re lucky! It means you’re using the fastest mobile Internet connection available on the globe at present. 4G is the fourth generation of mobile technology. It is also called LTE (Long Term Evolution). 4G connection works as good as a wi-fi connection of your home or office. With such a connection you can do everything on your mobile that you can do on your desktop. Just to round it all up, the bars in signal indicator show the strength or quality of the signal you’re getting at your present location. Also, mobile phone makers often use a dull color (like gray) to show weak / absent signal and a bright color (like green and blue) to show good signal. Tiny arrows in the signal bar show that the data transfer is taking place. The radar like icon shows the wi-fi connection. I hope this information was useful for you. Please feel free to ask should you have any questions on this topic. I will be happy to try and help. Thank you for using TechWelkin. When we see the E or H or H+ etc sign on the mobile, who actually generates the signal / how is the signal generated? How to know that the speed at a particular time is actually E/H/H+ etc. There is always a difference between data counted by mobile and service provider. Is there any sure-shot way to count the data downloaded/uploaded? As mentioned in the article, 100mbps is the theoretical limit. It is just the upper limit, it does not mean that service providers will necessarily provide this speed under 4G. 4G will not go beyond 100mbps but it can stay below this limit. Thanks for providing such important info. I only use the cell phone —but today I have the knowledge about the networks use. Such needful info. thanks I will share this article with everyone. have a good time!
![]()
![]()
![]()